Many businesses are dependent on personal data processing, and the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) requires ensuring strict security measures for it. Every organization handling the personal data of European Union (EU) users must perform a GDPR risk assessment to mitigate risks.
It’s important not just to ensure compliance and avoid hefty fines but to enhance security and protect your business reputation. This guide will provide you with the full process on how to conduct a GDPR risk assessment to help your business stay compliant and secure.
5 steps to conduct a risk assessment
A GDPR risk assessment is the process of evaluating and mitigating risks and threats to data security in order to demonstrate GDPR compliance efforts and adopt appropriate safeguards. To conduct a risk assessment, follow these steps:
Step 1: Map out the data
To perform a risk assessment, you first have to know what data you collect and where it comes from. The most convenient way is to document it all in one place. Here are the main points you have to consider:
- Understand how the data travels. You have to know all the channels that your business uses to collect data. This could be your website cookies, newsletter, or third-party integrations.
- Know what data is collected. Make a list of personal user data that is collected, such as names, email or IP addresses, financial data, or biometrics.
- Understand the purpose. Think of what is the lawful basis for processing specific data categories. According to GDPR Article 6, there are 6 lawful bases: explicit consent, contractual obligation, legal obligation, vital interests, public interest task, legitimate interest.
- Find out where data is stored. Know where your business stores all of the collected data. This could be a database or hard copy.
- Document who has access to data. Knowing who can view data helps ensure that only authorized access is permitted, strengthening security.
Step 2: Assess vulnerabilities and threats
Proper mapping out of data collection practices helps businesses identify vulnerabilities and potential threats. There are a few examples of internal and external risks that come with managing user data:
- Technical vulnerabilities, like outdated software or no encryption, which can result in data breaches or unauthorized access.
- Human errors, like weak passwords or no employee training.
When such threats happen, they violate the confidentiality and accountability principles listed under the GDPR Article 5. To prevent them, organizations need to review each data processing stage step by step. It helps discover vulnerabilities before they’re exploited and mitigate risks.
Step 3: Perform a risk and impact analysis
Next, you must conduct a risk and impact analysis to understand which threats are most important and need immediate attention. Here’s what you should review:
- Likelihood – think of how likely the risk is to happen to prioritize them by importance.
- Impact – determine what could be the damage caused by the identified risks. For example, this could be regulatory fines, reputational damage, etc.
- Risk level – discuss with your partners how you could measure risk severity and evaluate each risk.
Step 4: Adopt risk mitigation measures
Depending on the type of identified risks, you need to adopt security measures for risk mitigation. Here are a few examples of threat types and the technical and organizational measures you can adopt:
|
Threat type |
Example |
Prevention methods |
|
Ransomware |
Blackmail, encryption attacks |
Backups, employee awareness training |
|
Malware |
Virus, encryption attack, worm, blackmail |
Regular antivirus scanning, software updates |
|
Access misuse |
Identity theft or unauthorized access |
Two-factor authentication, strong passwords |
|
Data breach |
Hacking, phishing, accidental leaks |
Encryption, access control, network monitoring |
|
Employee errors |
Sending data to the wrong recipient, weak passwords |
Regular training |
According to GDPR Article 32, if a threat (like data breach) occurs, controllers must ensure restoration of data in a timely manner. The article also states that it’s necessary to regularly test the adopted technical and organizational measures.
Step 5: Document GDPR compliance
GDPR requires businesses to demonstrate compliance and accountability. This means that all data processing activities, risk and impact assessments, and mitigation measures must be documented. Let’s take a look at what exactly you need to document:
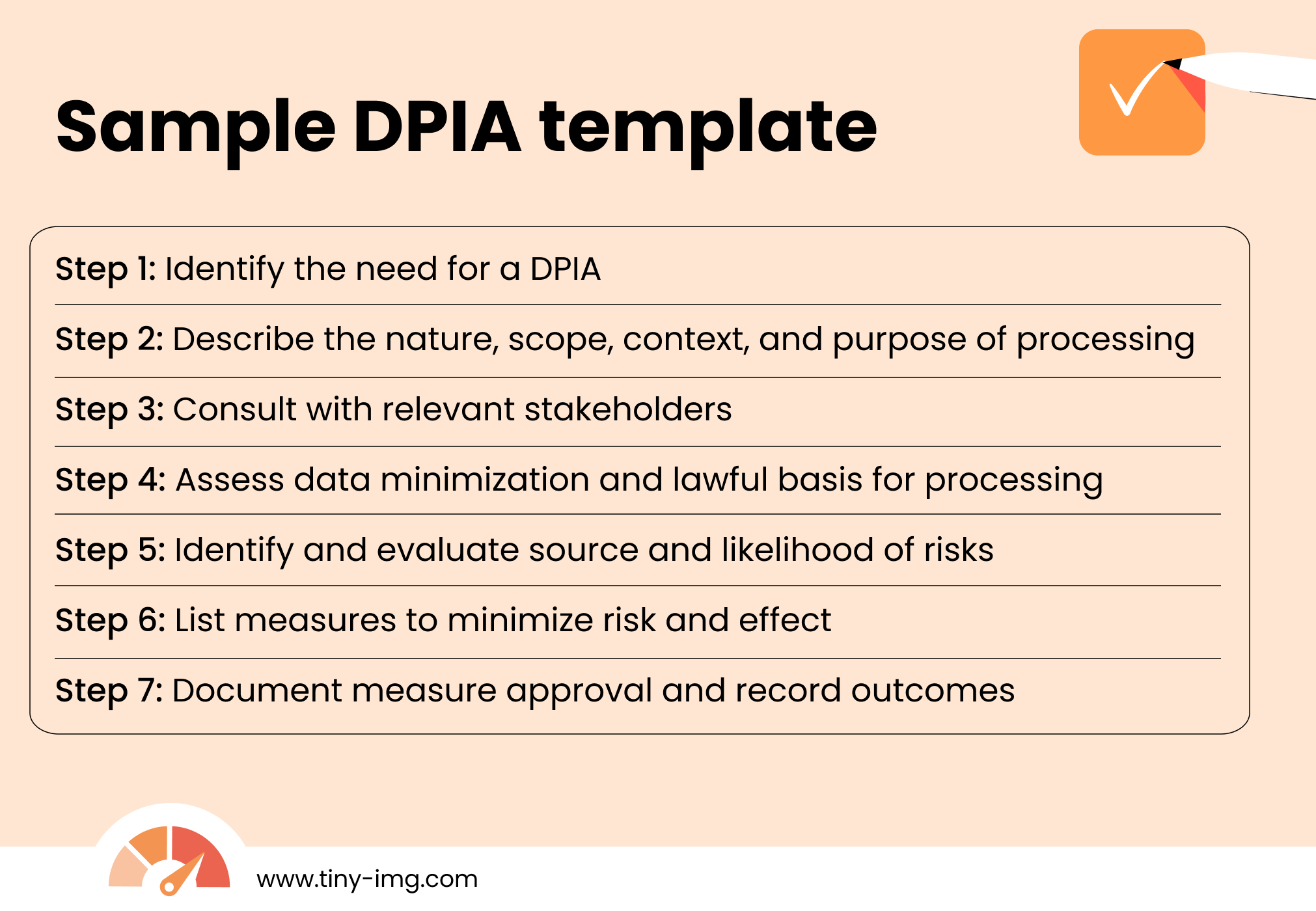
- Data Protection Impact Assessment (DPIA). If your business is handling sensitive data, like financial or health information, you need to conduct a DPIA. It includes documenting the purpose, scope, nature of your data collection practices, describing the risks, and listing mitigation measures.
- Processing activity records. As per GDPR Article 30, all controllers and processors must keep records of purposes for processing, data subject and personal data categories, data recipients, data erasure time limits, and description of technical and organizational security measures.
Why GDPR risk assessment is essential for your business
A GDPR risk assessment helps reduce the chance of threats, like data breaches, and helps improve user rights protection.The main reasons why a GDPR risk assessment is important include:
- GDPR compliance. The GDPR requires organizations to continuously document their processing activities, assess risks, and uphold the highest data security standards.
- Prevent risks. Assessing the vulnerabilities in your organization can help reduce the chances of threats. For example, you may find data breach, ransomware, or unauthorized access risks and implement security measures before they happen.
- Build user trust. By taking active measures to prevent threats and keep your customer data safe, you prevent damaging your business reputation. Instead, according to a survey by Cisco, 94% of users won’t buy from an organization if they don’t properly protect their data.
- Avoid regulatory fines. Risk assessment helps prevent large GDPR fines. Such threats like data breaches are considered serious violations, meaning the fines can go as high as €20 million, or 4% of the firm’s global annual revenue from the previous year (whichever is higher).
Tools and resources for effective GDPR risk assessment
To effectively conduct a GDPR risk assessment and ensure compliance, you can use additional tools and resources:
- Data mapping tools. You can leverage such software to create and track the personal data flow across systems.
- Threat detection software. Adopt tools that scan your system for vulnerabilities or offer security measures like encryption or access control.
- DPIA templates. Use an official DPIA template to help you evaluate and improve your highly sensitive data security.
- ISO standard compliance. Getting certification for international standards for security and privacy, such as ISO 27001 and ISO 27701 can help further improve data security beyond GDPR.
- Consent management platforms (CMPs). Use a consent management platform to gather and document all user consent in one place automatically.
Frequently asked questions
A GDPR risk assessment is the process of identifying and mitigating the threats and risks that come with the processing of personal data under the General Data Protection Regulation. Ensuring data security is one of the main requirements under the GDPR, which requires continuous monitoring and compliance.
According to GDPR Article 5, the main principles of GDPR are:
- Lawfulness, fairness, and transparency
- Purpose limitation
- Data minimization
- Accuracy
- Storage limitation
- Integrity and confidentiality
Data controllers must also be responsible for compliance with the main principles, demonstrating accountability.