The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is a privacy law created to protect the privacy of European Union (EU) residents. It gives users more control over how companies handle and share their data.
Companies that don’t comply with GDPR can face reputational damage and business-impeding fines. Non-severe violations can result in 2% of global annual revenue or €10 million, while severe breaches can reach 4% or €20 million respectively.
With a complete GDPR compliance checklist, you can protect the personal data of your website visitors and prevent penalties. It’s suitable for all companies to which the GDPR applies, whether you’re processing EU citizen data in the EU or outside of it.
What is GDPR?
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is a data privacy law that helps shape how companies collect, process, and handle the personal data of European Union individuals. Although it was implemented by the EU, it applies to all entities that process EU resident data.
The main goal of GDPR is for organizations to be transparent about their data processing practices and give users some level of control over what data is collected. On websites, this is usually achieved with a clear privacy policy and a data collection notice or cookie banner.
The GDPR came into effect in 2018 and has already been enforced on both large and small companies. For example, some of the biggest GDPR fines were given to Amazon – €746 million for failing to obtain user consent for targeted advertising. To avoid such penalties, businesses must ensure GDPR compliance.
Why is GDPR compliance important?
GDPR helps ensure that the personal data of users is collected and processed in a secure manner while following legal requirements, such as obtaining proper consent. Here are the main reasons why compliance with the GDPR is important for organizations:
- Protects data subject rights. The GDPR gives users control over how their personal data is handled, ensuring organizations respect their rights. This includes such rights as the right to access, be informed, rectify, erase, object, or restrict processing.
- Prevents data breaches. Complying with GDPR means that you secure the data of your users. This guarantees higher prevention of data breaches which could result in reputational and financial damage.
- Ensures customer trust. GDPR compliance ensures that organizations are transparent with their users, leading to higher trust. Meanwhile, misuse of personal data or data breaches can result in a loss of customers.
- Prevents fines. Refusing to comply with the GDPR can lead to warnings or a GDPR fine of up to 4% of the business’s total annual turnover or up to €20 million, whichever is higher. In extreme cases, it can lead to a temporary or permanent data ban.
10-step GDPR compliance checklist
Here are the main GDPR requirements to follow and stay compliant:
Step 1: Familiarize with GDPR principles
The GDPR outlines 7 principles that are foundational to compliant data collection and protection practices. They include:
- Lawfulness, fairness, and transparency. Always keep users informed on how their personal data will be used. Ensure your data handling practices are lawful and fair.
- Purpose limitation. Ensure your organization only collects data for specified purposes.
- Data minimization. Only collect data to the extent that is absolutely necessary.
- Accuracy. Make sure that the data you collect is up to date.
- Storage limitation. Avoid storing user data for longer periods than necessary.
- Integrity and confidentiality. Adopt proper personal data security measures to prevent unauthorized access or loss.
- Accountability. Organizations must demonstrate compliance and be responsible for their data handling practices.
Step 2: Appoint a Data Protection Officer (DPO)
A Data Protection Officer (DPO) is responsible for ensuring that a business processes personal data in compliance with the GDPR. Their duties include reviewing data processing activity compliance, checking policies, and conducting Data Protection Impact Assessments (DPIAs).
You need a DPO if data processing is handled by a public authority or your core activities include extensive data processing.
The DPO can be the company’s staff member or a person or organization outside of the company but under a contract. They must have expertise in data protection laws and a deep understanding of the GDPR.
Step 3: Audit collected personal data
To ensure proper GDPR compliance, you should conduct an in-depth audit of what personal data your business collects and processes. Here are the key points to consider when auditing your data:
Here are the key points to identify to create data flow maps:
- Data flow channels. Review how and where your collected data is flowing, such as from newsletter subscriptions or third-party integrations.
- Data categories. List all the information that is being collected, like names, email addresses, devices, IP addresses, and more.
- Data storage. Review how you store the information you collect, like a database or hard copy.
- Data access. Keep track of who has access to the collected data and don’t forget to review the security practices implemented to protect it.
- Data transfers. Document how data travels internally and when in possession of third parties to ensure data is not transferred outside the EU without complying with the GDPR.
After mapping out your data flows, ensure that your privacy policy states the appropriate lawful basis for processing.
Step 4: Provide a lawful basis for processing
Organizations must provide a legal basis for processing user data. According to GDPR Art. 6, there are 6 lawful bases:
- Explicit consent provided by the data subject
- To fulfill a contractual obligation if the user is an involved party
- To comply with a legal obligation
- To protect the vital interests of a user
- To carry out a task in the public interest
- For legitimate organizations or a third party’s interests
Make sure you also update your privacy policy stating the clear legal basis for collecting and processing data.
Step 5: Create a clear privacy policy
A privacy policy is a legally binding agreement that must inform users about how an organization collects and processes their personal data. It must be transparent and written in plain and simple language so any user can understand what they’re agreeing to.
Additionally, your privacy policy should be reviewed regularly and updated when needed. It should include information on what specific data is collected, how long, how it will be used, and who it will be shared with. It must also explain to users their rights.
You can check the official GDPR privacy policy template for specific requirements on what to include.
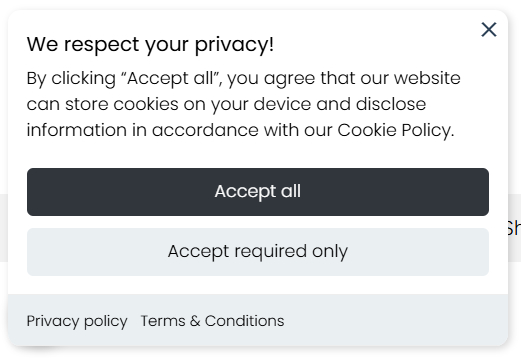
Step 6: Adopt a cookie banner
If your website uses non-essential cookies, you must obtain GDPR cookie consent. This is usually done with a cookie banner or popup. Let’s review the main consent requirements:
- Inform users of data collection. Use the cookie banner to clearly state that you’ll collect specific personal data and why if consent is granted. It must be written in simple-to-understand language.
- Include an opt-in button. Companies must provide a consent approval button and refrain from collecting data until the user accepts.
- Enable consent management. Give users control over their personal data and adopt granular consent. This means allowing users to choose which cookie categories they want to consent to.
- Provide a withdrawal option. Users have the right to withdraw consent at any time, so make the opt-out option easily accessible on your site.
- Link to the privacy policy. Organizations must place a link to the privacy policy in an easy-to-access place so that users can know what they’re consenting to.
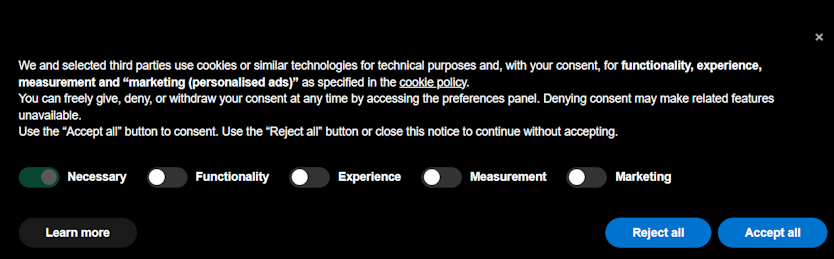
Here’s a simple example of how a GDPR-compliant consent banner should look like:
As you can see, it discloses the use of cookies and provides users with a level of control over their data by letting them choose which cookies to accept. Users can also either accept all or reject all cookies with a click of a button, and there’s also a link to the company’s cookie policy.
Step 7: Respect data subject rights
Organizations must create processes on how to handle subject access requests (SARs) within a timely manner. Some companies use a link in their website footer or include a separate page with information on how to manage personal data.
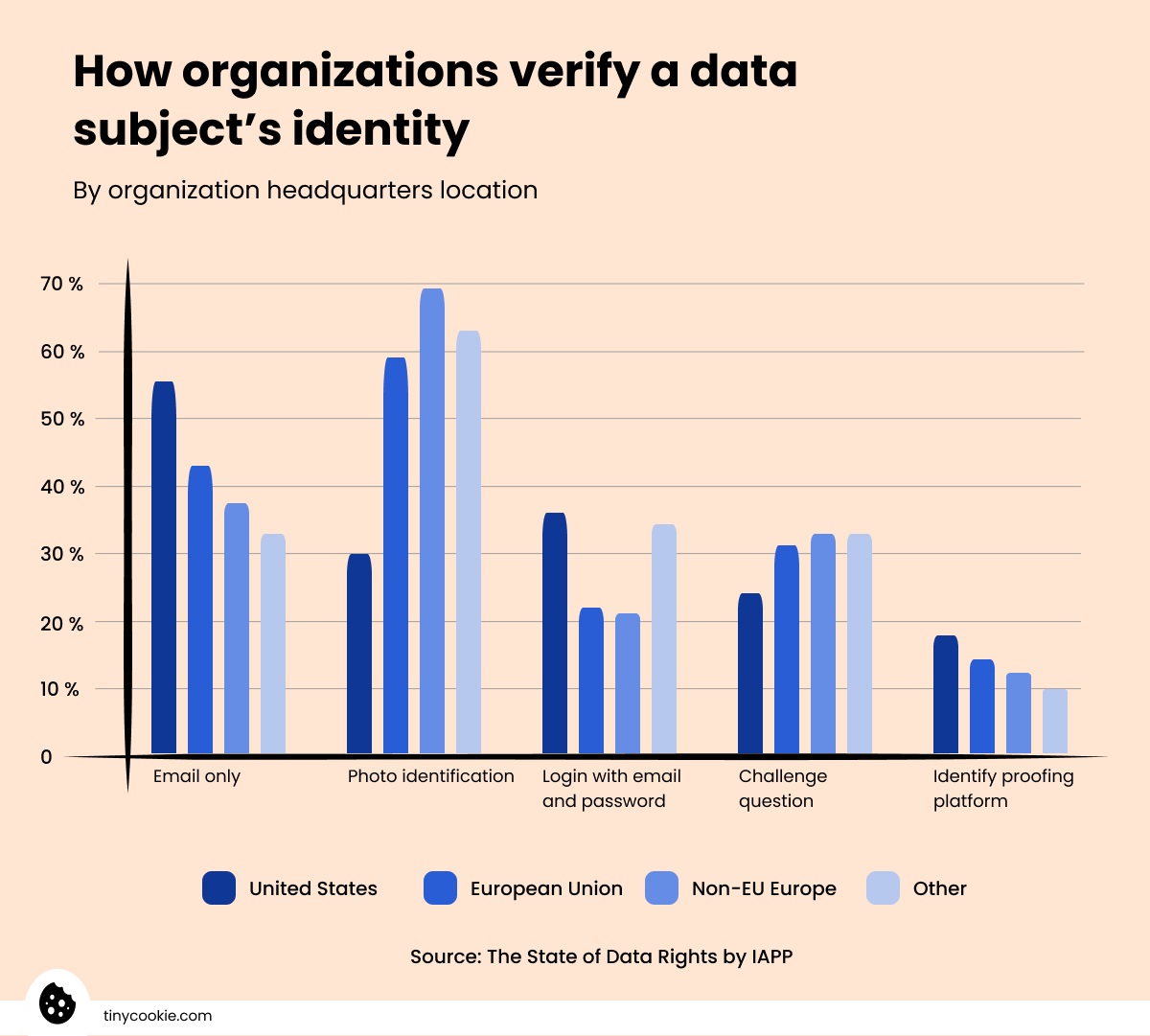
When data subjects request access to their personal data, the GDPR Recital 64 requires organizations to verify their identity for security reasons.
According to research by IAPP, the most popular ways to verify the user’s identity in Europe are photo identification, email, or challenge questions.
Organizations must respond or take action within one month of the request receipt. If the request is complex, the GDPR Art. 12 allows extending it by two months. In such cases, you must inform the data subject about the extension.
Step 8: Ensure data protection
GDPR Article 32 encourages organizations to take appropriate measures to ensure data security, both technical and organizational. Here are the main GDPR requirements:
- Data pseudonymization and encryption
- Data confidentiality, integrity, and resilience of systems
- Personal data access and availability restoration in the event of an incident
- Regular testing, assessments, and evaluation of adopted security measure effectiveness
There are many tools that can be used to secure data. For example, VPNs and firewalls can help ensure the organization’s network is safe from unauthorized system access.
Additionally, full-disk and end-to-end encryption can safeguard the data from the origin point to its destination. For preventing data loss in cases of hardware failures or cyberattacks, creating data backups is also a security measure.
Even when incidents happen, it’s important to be prepared. Organizations should adopt access and identity management tools as well as start monitoring user, entity, or third-party activities.
Step 9: Create a data breach response plan
It’s best to prepare your company for a data breach before it happens. Note that GDPR Art. 33 requires informing the supervisory authority with detailed data breach documentation in 72 hours to verify compliance.
Here are some of the main steps to ensure a good response plan:
- Assess your risks and assets to know what poses the biggest risks in your organization.
- Define response team responsibilities, including IT, HR, communications, and other departments.
- Ensure regular training so your response team members always understand their roles and are prepared.
- Adopt detection technologies, such as data-centric solutions and intrusion detection systems.
- Create an isolation plan which is important to contain affected systems.
- Document the incident in detail, from its nature to how it was contained and solved.
- Prepare a communication strategy, both internal and external, to ensure transparency and maintain user trust.
Step 10: Ensure third-party compliance
Proper GDPR compliance involves ensuring that your third-party services or partners are also compliant with the regulation. This means reviewing their privacy policies to understand how they handle user data.
If a third party handles personal data on your behalf, you must enter a Data Processing Agreement (DPA). It’s a legally binding contract that helps ensure lawful, secure, and compliant data processing by third parties.
A DPA should include such information as the purpose for processing, obligations of the processor, what data is collected, and data breach handling protocols.
- Tip: map out which vendors have access to what data and keep a log for easier third-party compliance management.
You can review a summarized GDPR compliance checklist below:
Common challenges in GDPR compliance
While the GDPR has clear main requirements for protecting the rights of user privacy, compliance isn’t always easy. For starters, with various third-party services, websites, and partners, auditing exact data flows can be challenging.
Additionally, the GDPR requires businesses to secure user personal data, but proper security measures aren’t specified. That’s why it’s better to obtain comprehensive security solutions, from endpoint protection to backup and recovery.
The compliance requirement list grows even wider for organizations transferring data outside the EU. For such cases, it’s useful to check what countries the European Commission has adopted adequacy decisions for. You can learn more in the international transfer requirement guide.
Frequently asked questions
Minor GDPR violations, such as not keeping data processing records, can result in a fine of up to €10 million, or 2% of the firm’s global annual revenue. More severe violations, like a data breach, can result in a fine of up to €20 million, or 4% of the firm’s global annual revenue from the previous financial year.
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) applies to any entity that collects or processes the personal data of EU residents. It must comply with GDPR requirements no matter where it operates.
It’s best that businesses review their GDPR compliance, including the privacy policy and terms of use, at least annually or more frequently. This helps ensure an accurate reflection of the company’s legal documents and practices at all times.
![How to comply with GDPR? [10 steps checklist]](https://tinycookie.com/images/blog/gdpr-compliance-checklist.png)